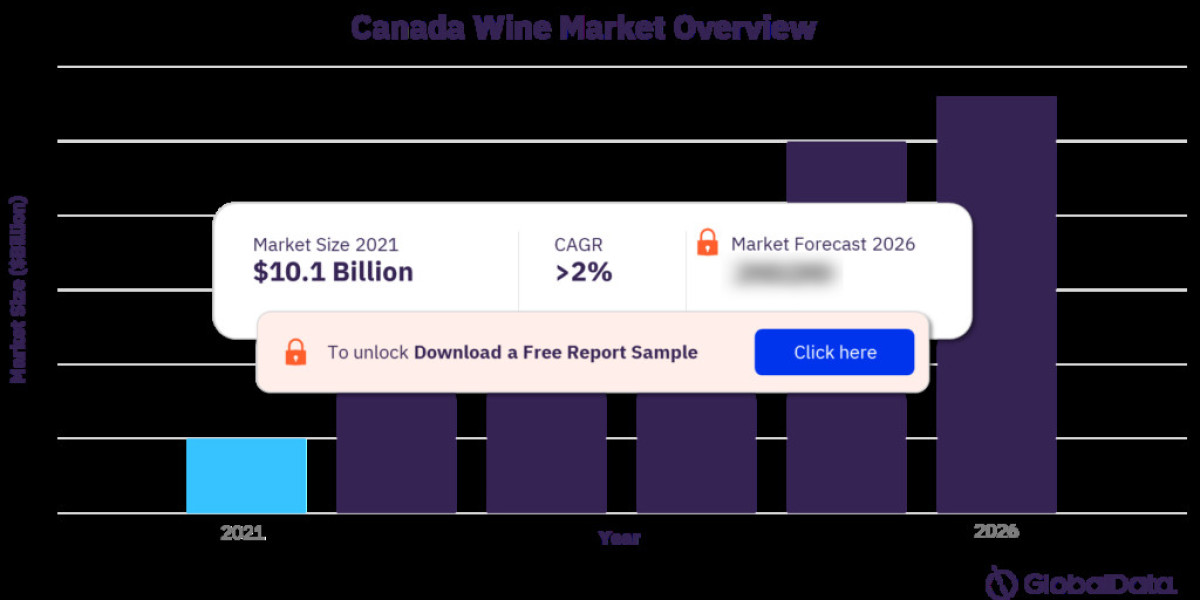
The Canadian wine industry, known for its crisp whites and bold reds, is increasingly embracing sustainable practices. Environmental responsibility is not just a trend; it's a necessity for attracting environmentally conscious consumers and ensuring the long-term viability of the industry.
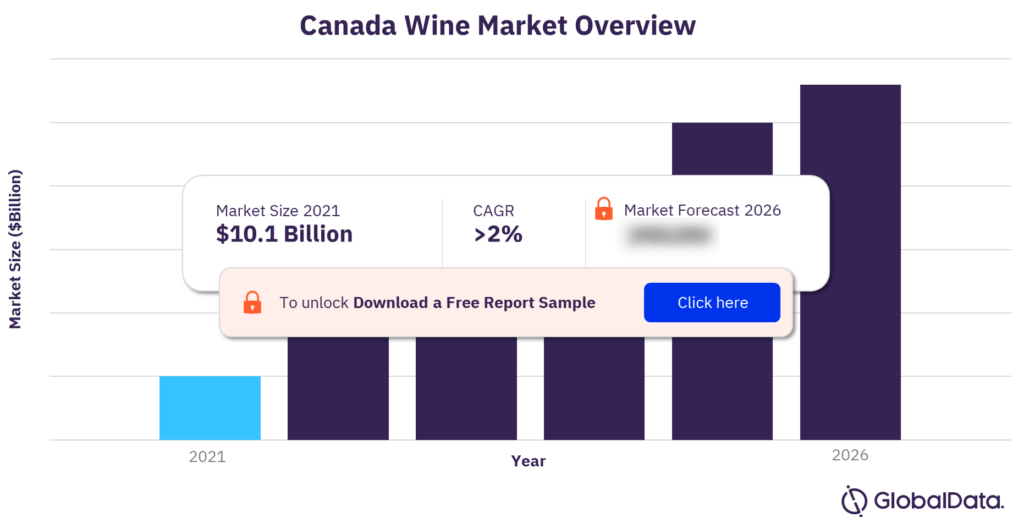 For more insights, download a free report sample
For more insights, download a free report sample
Here's a closer look at the key sustainability practices shaping the Canadian wine market:
Vineyard Management:
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): IPM strategies minimize reliance on chemical pesticides and herbicides by promoting natural predators and using organic alternatives for pest control. This protects biodiversity and reduces harmful environmental impact.
- Water Conservation: Water scarcity is a growing concern. Canadian wineries are implementing water-saving irrigation practices such as drip irrigation, using drought-resistant cover crops, and capturing rainwater for vineyard use.
- Soil Health and Sustainability: Healthy soil is essential for producing quality grapes. Wineries are adopting practices like cover cropping, composting, and no-till farming to improve soil health, fertility, and water retention.
- Biodiversity Promotion: Healthy vineyards foster biodiversity by creating habitats for beneficial insects and pollinators. Planting native wildflowers, hedgerows, and encouraging natural vegetation promotes biodiversity and a balanced ecosystem.
Winemaking Practices:
- Sustainable Winemaking Techniques: Minimizing energy consumption throughout the winemaking process, using energy-efficient equipment, and utilizing natural light for fermentation are key practices.
- Water Efficiency in Wine Production: Reducing water usage during winemaking through techniques like grape sorting, optimizing cleaning procedures, and reusing process water are crucial steps towards sustainability.
- Waste Reduction and Recycling: Composting grape pomace (skins and seeds), recycling glass bottles, and utilizing sustainable packaging materials are essential for minimizing waste and environmental footprint.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Wineries are increasingly investing in solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy sources to power their operations, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Certifications and Transparency:
- Third-Party Sustainability Certifications: Several sustainability certification programs exist, such as Sustainable Winegrowing British Columbia (SWBC) and VQA Wines of Canada's Sustainable Winegrowing program. These programs provide a framework for best practices and offer consumers assurance of a winery's commitment to sustainability.
- Transparency and Consumer Communication: Wineries are communicating their sustainability efforts more openly, through website disclosures, educational materials, and participation in sustainability initiatives. This transparency builds consumer trust and fosters a connection with environmentally conscious wine drinkers.
The Road Ahead
Sustainable practices are no longer a niche concern; they are becoming the norm in the Canadian wine industry. As environmental awareness grows, wineries that prioritize sustainability will be well-positioned for success. Consumer demand for eco-friendly wines is rising, and wineries that can demonstrate their commitment to responsible practices will attract a loyal customer base. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement in sustainability efforts, the Canadian wine industry can ensure a thriving future for generations to come, all while producing exceptional wines that respect the environment.