Managing blood glucose levels is a critical aspect of living with diabetes. Over the years, technology has made it easier for people to monitor their blood sugar at home, thanks to the development of modern glucose testing devices. These devices provide an efficient, accurate way to track blood sugar levels daily. In this article, we'll take an in-depth look at sugar test devices, explain how they work, and highlight the benefits of regular glucose monitoring.
What is a Blood Glucose Test Machine?
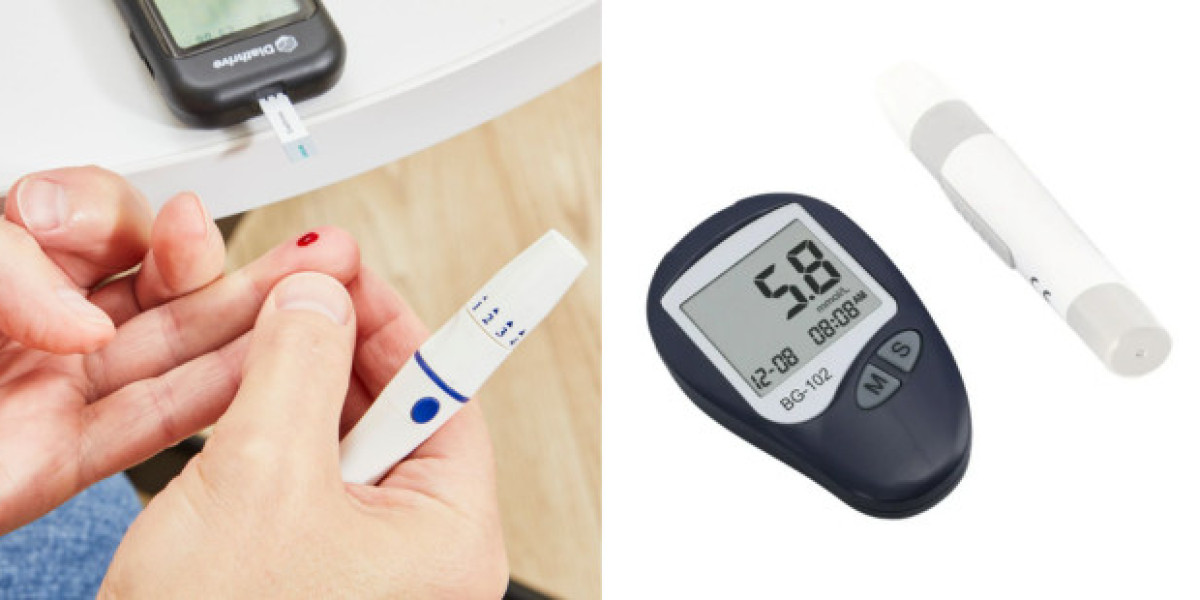
A blood glucose test machine, also known as a glucose testing device, is an electronic apparatus that measures the concentration of glucose (sugar) in your blood. These machines are essential tools for individuals with diabetes to maintain healthy blood glucose levels. The most common method involves pricking a finger with a lancet, applying a drop of blood to a test strip, and inserting it into the device for a quick reading.
Technological advancements have significantly improved these devices, making them more accurate, user-friendly, and portable. Many of these devices also come with digital displays, data storage features, and even smartphone integration, allowing users to keep track of their readings over time.
Why Blood Glucose Monitoring is Important
For people with diabetes, monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for managing the condition and preventing complications such as heart disease, stroke, nerve damage, and kidney failure. Keeping blood sugar within the recommended range can help reduce the risk of these complications. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends regular blood sugar checks to ensure glucose levels stay within target ranges.
Monitoring helps in:
- Understanding how diet, physical activity, and medication affect blood sugar.
- Adjusting insulin doses or other medications.
- Identifying trends in blood sugar levels.
- Preventing hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
Whether you use an older sugar test device or one of the latest smart monitors, frequent monitoring provides a clearer picture of your overall health.
Types of Glucose Testing Devices
There are several types of glucose testing devices available on the market, each designed to suit different needs. Let’s take a closer look at the most common ones:
1. Basic Glucometers
Basic glucose testing devices are simple to use, and they typically come with a lancet, test strips, and a meter to display the readings. Users prick their fingers, apply a drop of blood to a test strip, and insert the strip into the glucometer. The device then provides a blood sugar reading, often within seconds.
These devices are affordable, widely available, and reliable, making them ideal for daily blood glucose monitoring.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
A more advanced option is the Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM). Unlike traditional glucometers, CGMs track glucose levels throughout the day and night by using a small sensor inserted under the skin. The sensor continuously measures glucose in the interstitial fluid, which is the fluid surrounding the body’s cells, and sends the data to a monitor or smartphone.
CGMs provide real-time readings and alerts if blood sugar levels drop too low or rise too high. This type of sugar test device is excellent for individuals who need frequent monitoring or those who experience fluctuating glucose levels.
3. Non-Invasive Glucose Testing Devices
While most glucose tests require blood samples, there are also non-invasive devices in development that aim to measure glucose levels without needing to prick the skin. These devices use methods such as spectroscopy or sensors that detect glucose through the skin.
Although still in the early stages of development, non-invasive glucose testing devices may become a game changer for people who are looking to avoid the discomfort of finger pricks.
4. Smart Glucose Monitors
Smart glucose monitors sync with smartphones, allowing users to track their readings over time and share the data with healthcare providers. These devices often come with apps that offer valuable insights, graphs, and trends based on your readings. Some models even connect to apparatus for blood pressure, combining blood sugar and blood pressure monitoring in one convenient platform.
For tech-savvy users, a smart sugar test device with app integration provides a modern and efficient way to manage diabetes.
How to Use a Glucose Testing Device
Using a glucose testing device is relatively simple, though it may vary slightly depending on the type of device. Below are general steps for using a basic glucometer:
- Prepare the Device: Insert a test strip into the glucometer. Make sure your hands are clean and dry.
- Prick Your Finger: Use the lancet to prick the side of your fingertip. Squeeze your finger gently to obtain a small drop of blood.
- Apply Blood to the Test Strip: Place the drop of blood onto the test strip, ensuring it covers the required area.
- Read the Results: After a few seconds, the glucometer will display your blood glucose level. Write down the reading or let your device store it for future reference.
- Dispose of the Lancet and Strip: Safely discard the used lancet and test strip in a sharps container.
If you're using a CGM or smart monitor, the process is even easier, as the devices often read glucose levels automatically and send the data to your phone or computer.
Factors Affecting Blood Glucose Readings
It's important to understand that blood glucose readings can be influenced by a variety of factors, including:
- Food and Drink: Meals high in carbohydrates will cause a spike in blood sugar. Sugary drinks, snacks, or alcohol can also impact readings.
- Physical Activity: Exercise typically lowers blood sugar, but intense physical activity can sometimes lead to elevated glucose levels.
- Medications: Insulin, oral hypoglycemics, and other diabetes medications are designed to lower blood sugar. Skipping medication or taking the wrong dose can result in abnormal readings.
- Stress and Illness: Physical or emotional stress can raise blood sugar levels, as can certain illnesses like the flu or infections.
- Time of Day: Glucose levels tend to fluctuate throughout the day. For example, morning fasting blood sugar levels are often higher due to the body's natural circadian rhythm.
By regularly using a glucose testing device, individuals can identify trends and adjust their lifestyle, diet, and medication accordingly to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Features to Look for in a Sugar Test Device
Choosing the right sugar test device is important, as it will be an integral part of your daily health routine. Here are some features to consider when purchasing a blood glucose monitor:
1. Accuracy
The accuracy of the readings is paramount. Look for devices that are known for their reliability and have been approved by regulatory agencies like the FDA or CE.
2. Ease of Use
A device with a clear display, simple instructions, and easy-to-handle components is crucial for daily use. Devices that require less blood or offer painless testing are preferable.
3. Data Storage and Retrieval
Most modern glucometers can store previous readings. Some even allow you to download the data to your smartphone or computer. If you want to track your glucose trends over time, opt for a device with data storage or app integration.
4. Smart Features
Some glucose monitors come with smart features like Bluetooth connectivity, apps, and cloud-based data storage. This can be useful if you want to share data with your healthcare provider remotely or get automatic reminders to check your blood sugar.
5. Price and Affordability
The cost of glucose testing devices varies widely, especially when you factor in the price of test strips, lancets, and sensors. While basic glucometers are relatively inexpensive, CGMs and smart monitors tend to be more expensive. Make sure to pick a device that fits your budget without compromising on essential features.
6. Integration with Other Health Devices
Some advanced monitors integrate with other health devices, such as apparatus for blood pressure monitoring. This allows users to track multiple health metrics simultaneously, making it easier to manage diabetes and related conditions like hypertension.
Conclusion
Blood glucose monitoring is an essential part of managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. With the variety of glucose testing devices available today, there's a solution for everyone, from basic glucometers to advanced smart monitors. Regular monitoring provides valuable insights into how lifestyle, diet, and medication affect blood sugar levels, helping individuals with diabetes maintain better control over their condition.
Whether you're using a sugar test device for the first time or upgrading to a more advanced model, understanding how these machines work and how to use them effectively is key to managing your health. By incorporating the latest technology, such as smartphone apps and continuous glucose monitoring systems, you can stay informed and take proactive steps to manage your blood sugar levels, leading to a healthier, more active life.