The geocells market has grown steadily over the past decade, driven by increased demand for soil stabilization, erosion control, and load support solutions across a variety of sectors. Made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and other advanced polymers, geocells are used in civil engineering, construction, and environmental projects due to their ability to reinforce the ground, control erosion, and manage drainage. However, the market’s growth comes with its own set of challenges and opportunities. Understanding the dynamics of the geocells market, particularly its challenges and growth factors, is key to anticipating its future trajectory.
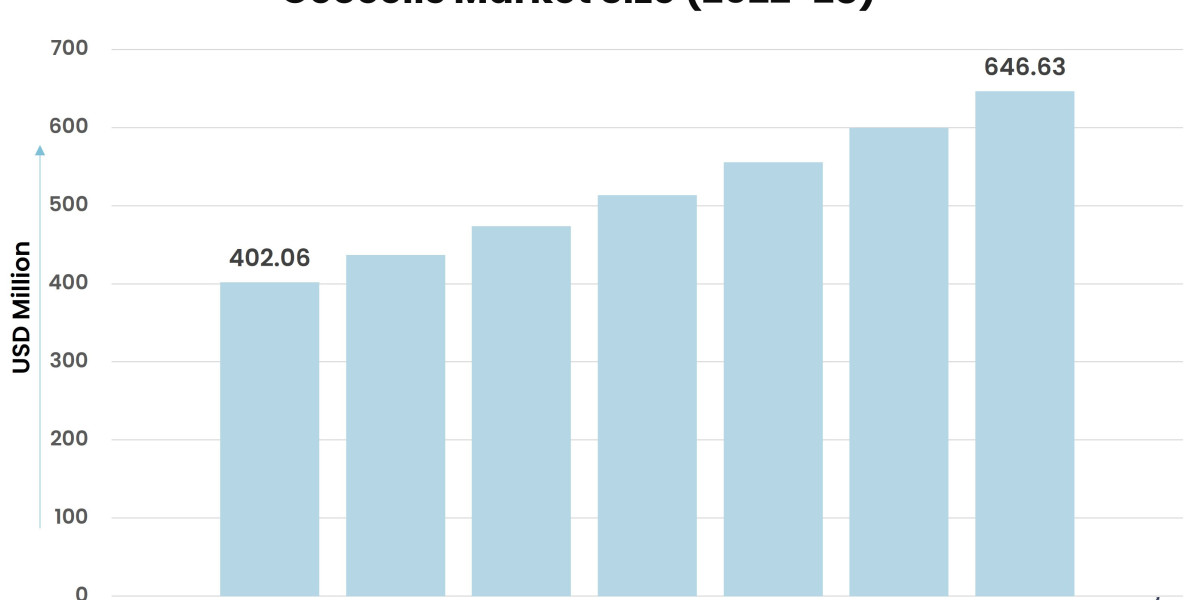
According to Stratview Research, the geocells market was estimated at USD 402.06 million in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 8.16% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 646.63 million in 2028.
Growth Factors
- Infrastructure Development and Urbanization
Rapid urbanization and infrastructure development, particularly in emerging economies like China, India, and Brazil, are significant growth drivers for the geocells market. Large-scale projects such as highways, railways, airports, and urban transit systems require reliable ground reinforcement, and geocells provide an ideal solution for stabilizing weak soils. With governments around the world investing heavily in infrastructure, the demand for geocells is expected to rise sharply in the coming years.
- Environmental Sustainability and Climate Change Adaptation
The growing emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly construction practices is another key factor driving the geocells market. Geocells allow for the use of local, low-quality materials as fill, reducing the need for expensive aggregates and minimizing the environmental impact of construction projects. Additionally, geocells are widely used for erosion control and flood prevention, making them valuable in climate change adaptation projects. As extreme weather events become more frequent, geocells are increasingly being used in flood management, coastal protection, and slope stabilization.
- Technological Advancements
Innovations in geocell materials and design are further boosting market growth. Advancements in polymer technology have improved the durability and strength of geocells, enabling them to withstand greater loads and perform better in harsh environmental conditions. Additionally, enhanced installation techniques are making geocells more efficient and cost-effective, expanding their use in diverse applications like renewable energy projects and environmental restoration.
Challenges
- High Initial Costs
Despite the benefits geocells offer, their relatively high initial costs can be a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly in cost-sensitive projects. Although geocells provide long-term savings through reduced maintenance and improved ground stabilization, the upfront investment can deter smaller contractors or governments working with tight budgets.
- Limited Awareness and Expertise
Another challenge facing the geocells market is limited awareness and expertise among contractors and engineers. In some regions, the adoption of geocells is slower due to a lack of familiarity with the technology and its benefits. This challenge is particularly evident in emerging markets, where traditional ground reinforcement techniques may still dominate.
Conclusion
The geocells market is poised for significant growth, driven by the need for advanced infrastructure, sustainable construction practices, and climate change mitigation. However, challenges such as high initial costs and limited awareness need to be addressed for the market to reach its full potential. As technological advancements continue to improve the performance and affordability of geocells, they will play an increasingly important role in the future of construction and environmental protection.