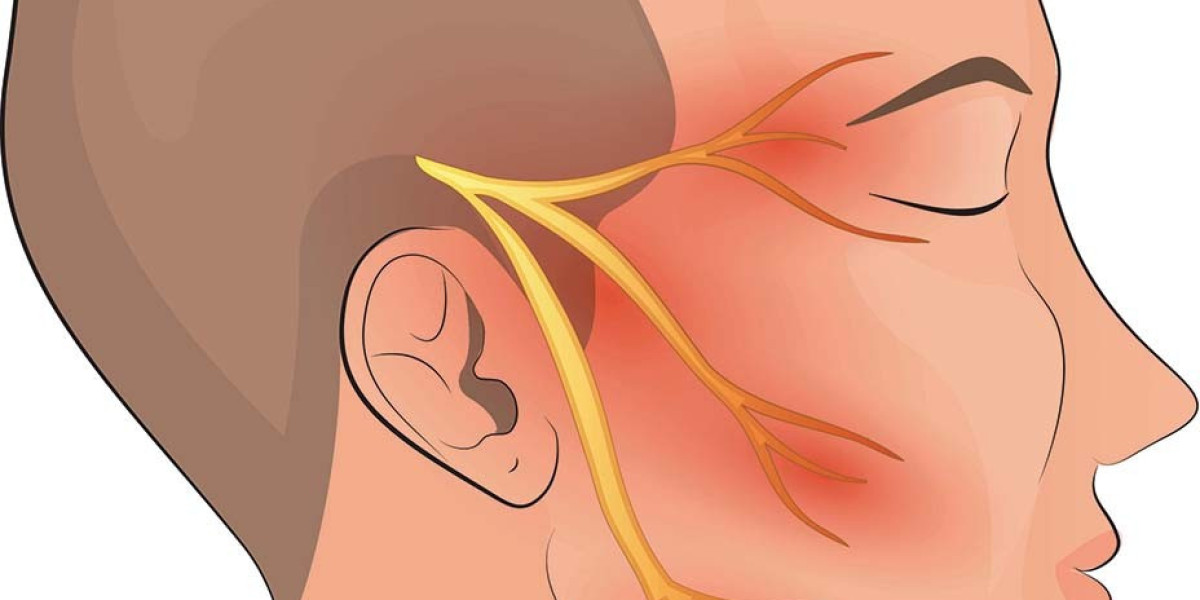
Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN) is a debilitating condition characterized by intense, stabbing pain in the face. It affects the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for transmitting sensory information from the face to the brain. This condition can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, causing excruciating pain that can be triggered by even the slightest touch or movement. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Trigeminal Neuralgia, providing valuable insights for those affected by this condition.
Prosoma 500mg is mostly formed of the active component carisoprodol. Carisoprodol is a muscle relaxant used to relieve muscular spasms and pain. It works by altering neuronal transmission in the central nervous system, which helps to relieve muscular discomfort and tension.
What Causes Trigeminal Neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia often occurs when the trigeminal nerve is compressed or irritated. This compression can result from various factors, including:
1. Blood Vessel Compression:
In many cases, trigeminal neuralgia is caused by the compression of the trigeminal nerve by nearby blood vessels. This pressure on the nerve can lead to episodes of intense pain.
2. Multiple Sclerosis:
Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis (MS) are at a higher risk of developing Trigeminal Neuralgia. The demyelination of nerves associated with MS can disrupt the normal functioning of the trigeminal nerve, leading to pain signals being misinterpreted by the brain.
3. Nerve Damage:
In some cases, damage to the trigeminal nerve due to injury or trauma can result in the development of Trigeminal Neuralgia. This damage can disrupt the normal transmission of sensory signals, leading to pain sensations.
Recognising the Symptoms
The hallmark symptom of Trigeminal Neuralgia is sudden, severe facial pain that can be triggered by activities such as eating, talking, or even touching the face lightly. Other common symptoms may include:
- Burning or Tingling Sensations: Some individuals may experience a burning or tingling sensation in the affected areas of the face.
- Episodic Pain: The pain associated with Trigeminal Neuralgia often occurs in sudden, brief episodes that can last from a few seconds to several minutes.
- Trigger Points: Certain trigger points on the face, such as the lips, cheeks, or jaw, may elicit pain when stimulated.
Prosoma 350mg is generally used as a muscle relaxant. Its primary element is carisoprodol, which acts by inhibiting pain signals between neurons and the brain. It is often recommended for the temporary alleviation of acute musculoskeletal pain or discomfort. Prosoma 350mg should be taken with caution and under the supervision of a healthcare expert, since it has habit-forming properties and may produce drowsiness or dizziness.
Exploring Treatment Options
While there is no cure for Trigeminal Neuralgia, several treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life for affected individuals. These may include:
1. Medications:
- Anticonvulsants: Medications such as carbamazepine or oxcarbazepine are often prescribed to help reduce the frequency and intensity of pain episodes.
- Muscle Relaxants: Drugs like baclofen may be used to alleviate muscle spasms and reduce pressure on the trigeminal nerve.
2. Surgical Interventions:
- Microvascular Decompression: In cases where Trigeminal Neuralgia is caused by blood vessel compression, microvascular decompression surgery may be recommended to relieve pressure on the trigeminal nerve.
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: This non-invasive procedure uses focused radiation to target and damage the trigeminal nerve, reducing pain signals.
3. Nerve Blocks:
- Glycerol Injection: A glycerol injection into the trigeminal nerve can temporarily block pain signals, providing relief from symptoms.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: This procedure uses heat to damage the trigeminal nerve, interrupting pain signals and providing long-term pain relief.
Living with Trigeminal Neuralgia
Managing Trigeminal Neuralgia can be challenging, but with the right treatment approach and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. It's essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and symptoms.
In addition to medical interventions, lifestyle modifications such as stress reduction techniques, maintaining a healthy diet, and avoiding trigger factors can also help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Conclusion
Trigeminal Neuralgia is a complex condition that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, those affected by this condition can take proactive steps to manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. With ongoing research and advancements in medical technology, there is hope for better management and treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia in the future.