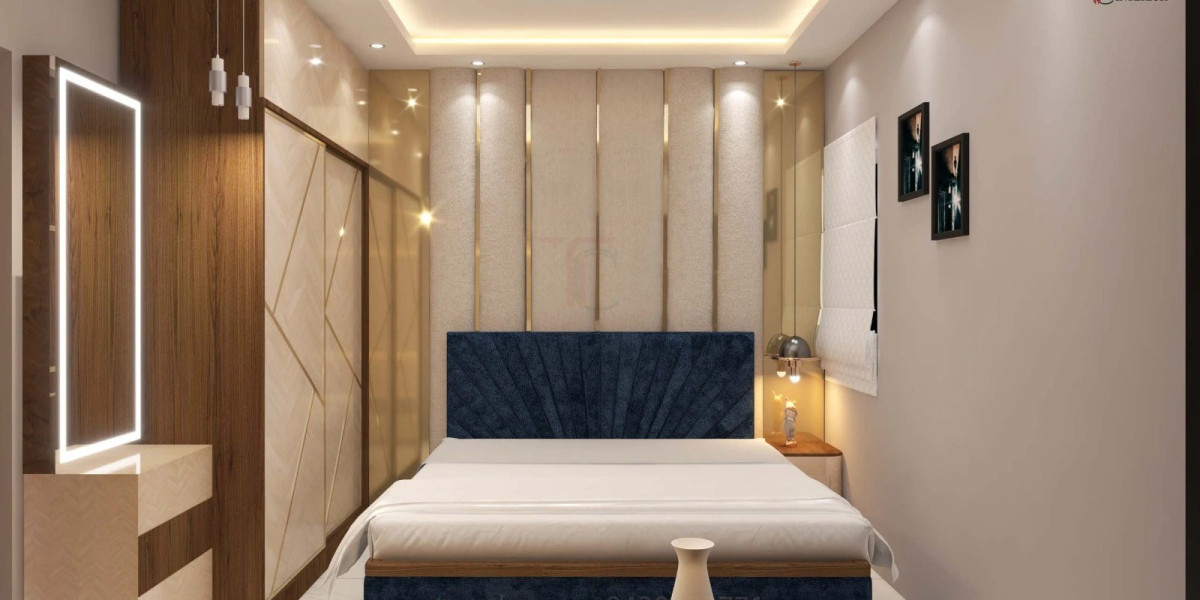
Isometric drawings, utilized extensively by architects and designers, stand out as a premier method for visualizing architectural concepts and ideas. These drawings offer a three-dimensional representation of an architectural project, enabling clients and stakeholders to gain a comprehensive understanding of the design and its spatial dynamics. In this section, we will explore the benefits of isometric drawings and their role in architecture.
Isometric drawings are an essential tool in the architectural design process. They provide a lifelike representation of an architectural project, allowing clients to visualize the structure's placement in its surrounding environment. This detailed view allows for better communication between architects, clients, and other stakeholders involved in the project.
Understanding Isometric Projection
Isometric drawings are created using a technique called isometric projection. This method involves drawing the three-dimensional object on a two-dimensional surface by projecting all of its lines onto the same angle. This results in an accurate representation of the object's depth, height, and width, unlike other forms of projection that can distort these dimensions.
What is Isometric Drawing?
An isometric drawing, a crucial type of pictorial representation, showcases an object in three dimensions. Distinctively, it employs a 30-degree angle to create a visually realistic portrayal of the object, displaying all three axes (x, y, z) in a manner where each is visible and equally scaled.
This approach contrasts sharply with traditional two-dimensional drawings by offering a depiction that more closely mirrors the object's appearance in reality, thereby providing a deeper insight into the design's actual spatial experience.
Advantages of Isometric Drawings
Employing isometric drawings in architectural projects brings numerous benefits:
- Visualization: They render a lifelike view of the design, significantly enhancing the ability of clients and stakeholders to visualize the project with a detailed perspective.
- Clarity: The representation of all three axes simplifies the understanding of spatial relationships among different components, elucidating how various elements are integrated within the design.
- Accuracy: Isometric drawings outshine traditional two-dimensional drawings in precision, depicting the true proportions and dimensions of objects, which is critical for assessing the feasibility and integrity of a design.
- Communication: Serving as a universal visual language in the architecture and design sectors, isometric drawings facilitate smoother communication and collaboration across different teams and stakeholders, ensuring a coherent understanding of the project.
How to Create an Isometric Drawing?
The creation of isometric drawings entails a blend of artistic skill and technical knowledge. Here are the foundational steps to get started:
- Begin with sketching three orthographic views (front, top, and side) of the object on a specialized grid, designed to support isometric projection.
- Extend construction lines at a precise 30-degree angle from each corner of the object's base, laying the groundwork for an accurate spatial framework.
- Utilize these lines to outline an isometric box that defines the object's overall dimensions and shape, which acts as a scaffold for the detailed drawing.
- Proceed to add detailed elements and features, employing guidelines and precise measurements to ensure the drawing reflects the true characteristics of the object.
Tips for Creating Isometric Drawings
- Employing a grid is pivotal for maintaining consistency and precision throughout the drawing process.
- Consideration of line weight adds depth and perspective, with thicker lines suggesting proximity and thinner lines indicating distance.
- Incorporation of hidden lines provides clarity by revealing the interaction between various elements, enhancing the drawing's comprehensibility.
- Like any refined skill, proficiency in creating isometric drawings is achieved through continuous practice and dedication, coupled with a willingness to learn and adapt.
Conclusion
Isometric drawings are indispensable in the realm of architecture and design, offering a powerful medium for visualizing, communicating, and comprehending complex three-dimensional spaces. Mastery of isometric drawing techniques, accompanied by an understanding of its principles, empowers architects and designers to produce precise and compelling visual representations of their concepts, ultimately facilitating the realization of their visionary projects.