This article delves into the current state of South Africa's healthcare market, exploring its strengths, weaknesses, and the transformative potential of the proposed National Health Insurance (NHI) scheme.
The Current Landscape: Public vs. Private Divide
South Africa's healthcare system is divided between a public sector, serving roughly 80% of the population, and a private sector catering to the remaining 20%. The public sector, funded largely through government allocations, struggles with resource constraints, leading to long waiting times, staff shortages, and limited access to specialized treatments.
In contrast, the private sector offers a wider range of services, sophisticated medical technology, and shorter waiting times. This disparity is financed through private medical schemes, which act as a form of health insurance for employed individuals or those who can afford the premiums.
Market Size and Growth Potential
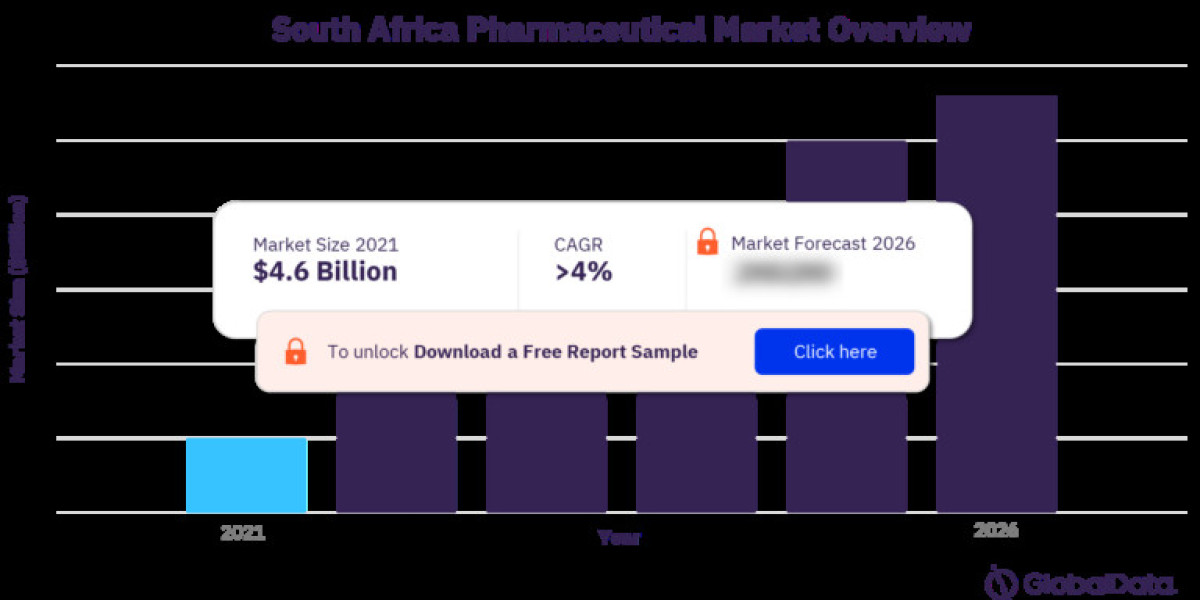
Despite these inequalities, the South African healthcare market is substantial and projected for further growth. In 2017, healthcare spending reached ZAR 414.5 billion (USD 31.1 billion), with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.4% anticipated over the next five years [3]. This growth is driven by factors such as rising incomes, an aging population, and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases like diabetes and HIV/AIDS.
The pharmaceutical sector is a key driver of this growth, with South Africa boasting the largest pharmaceutical market in Sub-Saharan Africa. The market is dominated by prescription drugs, with generic medications gaining traction due to their affordability [1].
Challenges and Opportunities
South Africa's healthcare market faces several challenges. The public sector's resource constraints limit access to quality care for a large portion of the population. Additionally, the fragmented nature of the private sector can lead to inefficiencies and high costs.
However, these challenges also present opportunities. The NHI scheme, currently in its development phase, aims to address these issues by creating a universal healthcare system that provides equitable access to quality care for all South Africans. The NHI is expected to increase demand for generic drugs, boost healthcare infrastructure development, and potentially stimulate local pharmaceutical production [1].
The National Health Insurance (NHI): A Game Changer?
The NHI is a highly debated yet potentially transformative policy. Proponents argue that it will reduce healthcare inequalities, improve access to services, and promote preventative care. The NHI is expected to be funded through a combination of increased government allocation, payroll taxes, and potential contributions from medical schemes.
However, concerns remain regarding the feasibility of the NHI. The financial sustainability of the scheme and its potential impact on the private sector are key areas of debate. Effective implementation will require careful planning, robust governance, and collaboration between public and private stakeholders.
Innovation and Technology: Shaping the Future
Technological advancements are also shaping the future of South Africa's healthcare market. Telemedicine, for example, has the potential to improve access to care in remote areas. Additionally, the rise of digital health solutions can enhance data management, streamline administrative processes, and empower patients to manage their health more effectively.
Conclusion: A Market on the Cusp of Transformation
South Africa's healthcare market stands at a crossroads. The existing inequalities are unsustainable, and the NHI presents an ambitious yet uncertain path towards a more equitable system. While challenges remain, the potential for positive change is significant. Embracing innovation and fostering collaboration between public and private stakeholders will be crucial in determining the success of the NHI and shaping a brighter future for South Africa's healthcare landscape.
Word count: Approximately 650 words
Additional Points to Consider for a 2000-word article:
- Expand on specific challenges faced by the public healthcare system, including staff shortages, infrastructure limitations, and the burden of communicable diseases.
- Discuss the role of private medical schemes in greater detail, exploring their financing models, service offerings, and potential impact under the NHI.
- Analyze the potential impact of the NHI on different stakeholders, including patients, healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, and medical scheme operators.
- Provide a more in-depth examination of the technological advancements transforming South Africa's healthcare sector, including telemedicine, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics.
- Include case studies or real-world examples to illustrate the challenges and opportunities within the South African healthcare market.
- Conclude with a future outlook, outlining potential scenarios for the development of the healthcare market under different NHI implementation strategies.
For more insights on South Africa's healthcare market, download a free sample report